The way that eels migrate along rivers and seas is mesmerising. There has been scientific agreement since the turn of the 20th Century that the Sargasso Sea is the breeding home to the sole European species. But it has taken more than two centuries since Carl Linnaeus gave this snake-shaped fish its scientific name before an adult was discovered in the area where they mate and spawn.
Even among nomadic people, the average human walks no more than a few dozen kilometres in a single trip. In comparison, the animal kingdom is rife with migratory species that traverse continents, oceans, and even the entire planet (1).
The European eel (Anguilla anguilla) is an outstanding example. Adults migrate up to 5000 km from the rivers and coastal wetlands of Europe and northern Africa to reproduce, lay their eggs, and die in the Sargasso Sea — an algae-covered sea delimited by oceanic currents in the North Atlantic.

As larvae emerge, they drift with the prevailing marine currents over the Atlantic to the European and African coasts (2). The location of the breeding area was unveiled in the early 20th Century as a result of the observation that the size of the larvae caught in research surveys gradually decreased from Afro-European land towards the Sargasso Sea (3, 4). Adult eels had been tracked by telemetry in their migration route converging on the Azores Archipelago (5), but none had been recorded beyond until recently.
Crossing the Atlantic
To complete this piece of the puzzle, Rosalind Wright and collaborators placed transmitters in 21 silver females and released them in the Azores (6). These individuals travelled between 300 and 2300 km, averaging 7 km each day. Five arrived in the Sargasso Sea, and one of them, after a swim of 243 days (from November 2019 to July 2020), reached what for many years had been the hypothetical core of the breeding area (3, 4). It is the first direct record of a European eel ending its reproductive journey.
Eels use the magnetic fields in their way back to the Sargasso Sea and rely on an internal compass that records the route they made as larvae (7). The speed of navigation recorded by Wright is slower than in many long-distance migratory vertebrates like birds, yet it is consistent across the 16 known eel species (8).

Wright claimed that, instead of swiftly migrating for early spawning, eels engage in a protracted migration at depth. This behaviour serves to conserve their energy and minimises the risk of dying (6). The delay also allows them to reach full reproductive potential since, during migration, eels stop eating and mobilise all their resources to swim and reproduce (9).
Other studies have revealed that adults move in deep waters in daylight but in shallow waters at night, and that some individuals are faster than others (3 to 47 km per day) (5). Considering that (i) this fish departs Europe and Africa between August and December and (ii) spawning occurs in the Sargasso Sea from December to May, it is unknown whether different individuals might breed 1 or 2 years after they begin their oceanic migration.
Management as complex as life itself
The European eel started showing the first signs of decline at the end of the 19th Century (10, 11). In 2008, the species was listed as Critically Endangered by the IUCN, and its conservation status has since remained in that category — worse than that of the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) or the Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus).
Read the rest of this entry »











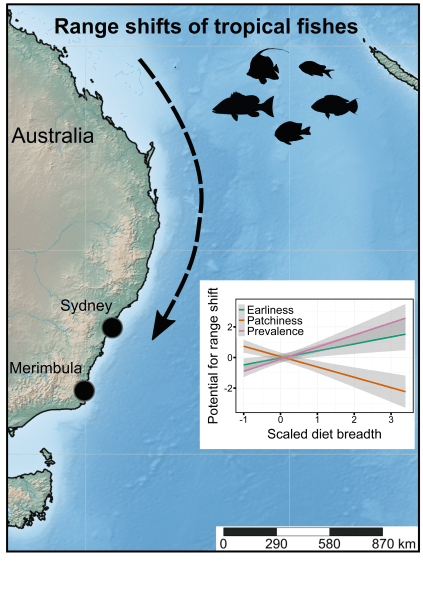 Ecologists often rely on measuring certain elements of a species’ characteristics, behaviour, or morphology to determine if these — what we call ‘traits’ — give them certain capacities to exploit their natural environments. While sometimes a bit arbitrarily defined, the traits that can be measured are many indeed, and sometimes they reveal rather interesting elements of a species’ resilience in the face of environmental change.
Ecologists often rely on measuring certain elements of a species’ characteristics, behaviour, or morphology to determine if these — what we call ‘traits’ — give them certain capacities to exploit their natural environments. While sometimes a bit arbitrarily defined, the traits that can be measured are many indeed, and sometimes they reveal rather interesting elements of a species’ resilience in the face of environmental change.

 it’s a provocative title, I agree. But then again, it’s true.
it’s a provocative title, I agree. But then again, it’s true.









The very worn slur of “neo-Malthusian”
7 09 2021After the rather astounding response to our Ghastly Future paper published in January this year (> 443,000 views and counting; 61 citations and counting), we received a Commentary that was rather critical of our article.
We have finally published a Response to the Commentary, which is now available online (accepted version) in Frontiers in Conservation Science. Given that it is published under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY), I can repost the Response here:
In their comment on our paper Underestimating the challenges of avoiding a ghastly future, Bluwstein et al.2 attempt to contravene our exposé of the enormous challenges facing the entire human population from a rapidly degrading global environment. While we broadly agree with the need for multi-disciplinary solutions, and we worry deeply about the inequality of those who pay the costs of biodiversity loss and ecological collapse, we feel obligated to correct misconceptions and incorrect statements that Bluwstein et al.2 made about our original article.
After incorrectly assuming that our message implied the existence of “one science” and a “united scientific community”, the final paragraph of their comment contradicts their own charge by calling for the scientific community to “… stand in solidarity”. Of course, there is no “one science” — we never made such a claim. Science is by its nature necessarily untidy because it is a bottom-up process driven by different individuals, cultures, perspectives, and goals. But it is solid at the core. Scientific confluence is reached by curiosity, rigorous testing of assumptions, and search for contradictions, leading to many — sometimes counter-intuitive or even conflicting — insights about how the world works. There is no one body of scientific knowledge, even though there is good chance that disagreements are eventually resolved by updated, better evidence, although perhaps too slowly. That was, in fact, a main message of our original article — that obligatory specialisation of disparate scientific fields, embedded within a highly unequal and complex socio-cultural-economic framework, reduces the capacity of society to appreciate, measure, and potentially counter the complexity of its interacting existential challenges. We agree that scientists play a role in political struggles, but we never claimed, as Bluwstein et al.2 contended, that such struggles can be “… reduced to science-led processes of positive change”. Indeed, this is exactly the reason our paper emphasized the political impotence surrounding the required responses. We obviously recognize the essential role social scientists play in creating solutions to avoid a ghastly future. Science can only provide the best available evidence that individuals and policymakers can elect to use to inform their decisions.
We certainly recognise that there is no single policy or polity capable of addressing compounding and mounting problems, and we agree that that there is no “universal understanding of the intertwined socio-ecological challenges we face”. Bluwstein et al.2 claimed that we had suggested scientific messaging alone can “… adequately communicate to the public how socio-ecological crises should be addressed”. We did not state or imply such ideas of unilateral scientific power anywhere in our article. Indeed, the point of framing our message as pertaining to a complex adaptive system means that we cannot, and should not, work towards a single goal. Instead, humanity will be more successful tackling challenges simultaneously and from multiple perspectives, by exploiting manifold institutions, technologies, approaches, and governances to match the complexity of the predicament we are attempting to resolve.
Read the rest of this entry »Share:
Comments : Leave a Comment »
Tags: commentary, complex adaptive system, consumption, critique, human population, Malthusian, neo-Malthusian, over-population, overshoot, Population
Categories : agriculture, anthropocene, biodiversity, climate change, demography, economics, education, Endarkenment, environmental economics, environmental policy, extinction, food, governance, human overpopulation, poverty, science, societies, sustainability