I should have published these ages ago, but like many things I have should have done earlier, I didn’t.
I should have published these ages ago, but like many things I have should have done earlier, I didn’t.
I also apologise for a bit of silence over the past week. After coming back from the ESP Conference in Portland, I’m now back at Stanford University working with Paul Ehrlich trying to finish our book (no sneak peaks yet, I’m afraid). I have to report that we’ve completed about about 75 % it, and I’m starting to feel like the end is in sight. We hope to have it published early in 2013.
So here they are – the latest 9 PhD offerings from us at the Global Ecology Laboratory. If you want to get more information, contact the first person listed as the first supervisor at the end of each project’s description.
—
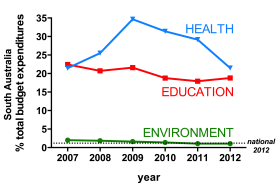
1. Optimal survey and harvest models for South Australian macropods (I’ve advertised this before, but so far, no takers):
The South Australia Department of Environment, Water and Natural Resources (DEWNR) is custodian of a long-term macropod database derived from the State’s management of the commercial kangaroo harvest industry. The dataset entails aerial survey data for most of the State from 1978 to present, annual population estimates, quotas and harvests for three species: red kangaroo (Macropus rufus), western grey kangaroo (Macropus fuliginosus), and the euro (Macropus robustus erubescens).
DEWNR wishes to improve the efficiency of surveys and increase the precision of population estimates, as well as provide a more quantitative basis for setting harvest quotas.
We envisage that the PhD candidate will design and construct population models:
- to predict population size/densities with associated uncertainty, linking fluctuations to environmental variability (including future climate change projections)
- to evaluate the efficiency of spatially explicit aerial surveys
- to estimate demographic parameters (e.g., survival rate) from life tables and
- to estimate spatially explicit sustainable harvest quotas
Supervisors: me, A/Prof. Phill Cassey, Dr Damien Fordham, Dr Brad Page (DEWNR), Professor Michelle Waycott (DEWNR).
2. Correcting for the Signor-Lipps effect
The ‘Signor-Lipps effect’ in palaeontology is the notion that the last organism of a given species will never be recorded as a fossil given the incomplete nature of the fossil record (the mirror problem is the ‘Jaanusson effect’, where the first occurrence is delayed past the true time of origination). This problem makes inference about the timing and speed of mass extinctions (and evolutionary diversification events) elusive. The problem is further complicated by the concept known as the ‘pull of the recent’, which states that the more time since an event occurred, the greater the probability that evidence of that event will have disappeared (e.g., erased by erosion, hidden by deep burial, etc.).
In a deep-time context, these problems confound the patterns of mass extinctions – i.e., the abruptness of extinction and the dynamics of recovery and speciation. This PhD project will apply a simulation approach to marine fossil time series (for genera and families, and some individual species) covering the Phanerozoic Aeon, as well as other taxa straddling the K-T boundary (Cretaceous mass extinction). The project will seek to correct for taphonomic biases and assess the degree to which extinction events for different major taxa were synchronous.
The results will also have implications for the famous Sepkoski curve, which describes the apparent logistic increase in marine species diversity over geological time with an approximate ‘carrying capacity’ reached during the Cenozoic. Despite recent demonstration that this increase is partially a taphonomic artefact, a far greater development and validation/sensitivity analysis of underlying statistical models is needed to resolve the true patterns of extinction and speciation over this period.
The approach will be to develop a series of models describing the interaction of the processes of speciation, local extinction and taphonomic ‘erasure’ (pull of the recent) to simulate how these processes interact to create the appearance of growth in numbers of taxa over time (Sepkoski curve) and the abruptness of mass extinction events. The candidate will estimate key parameters in the model to test whether the taphonomic effect is strong enough to be the sole explanation of the apparent temporal increase in species diversity, or whether true diversification accounts for this.
Supervisors: me, Prof. Barry Brook
3. Genotypic relationships of Australian rabbit populations and consequences for disease dynamics
Historical evidence suggests that there were multiple introduction events of European rabbits into Australia. In non-animal model weed systems it is clear that biocontrol efficacy is strongly influenced by the degree of genetic diversity and number of breed variants in the population.
The PhD candidate will build phylogenetic relationships for Australian rabbit populations and develop landscape genetic models for exploring the influence of myxomatosis and rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) on rabbit vital rates (survival, reproduction and dispersal) at regional and local scales. Multi-model synthesis will be used to quantify the relative roles of environment (including climate) and genotype on disease prevalence and virulence in rabbit populations.
Supervisors: A/Prof Phill Cassey, Dr Damien Fordham, Prof Barry Brook Read the rest of this entry »
-34.917731
138.603034


 If you live in South Australia, and in Adelaide especially, you would have had to be living under a rock not to have heard of the Great Koala Counts
If you live in South Australia, and in Adelaide especially, you would have had to be living under a rock not to have heard of the Great Koala Counts  Well, the data are in for GKC2 and we need help to analyse them. Just as a little reminder, the GKCs are designed to provide
Well, the data are in for GKC2 and we need help to analyse them. Just as a little reminder, the GKCs are designed to provide  Last year I wrote what has become a highly viewed post here at ConservationBytes.com about the
Last year I wrote what has become a highly viewed post here at ConservationBytes.com about the