Many animals avoid contact with people. In protected areas of the African savanna, mammals flee more intensely upon hearing human conversations than when they hear lions or sounds associated with hunting. This fear of humans affects how species use and move in their habitat.
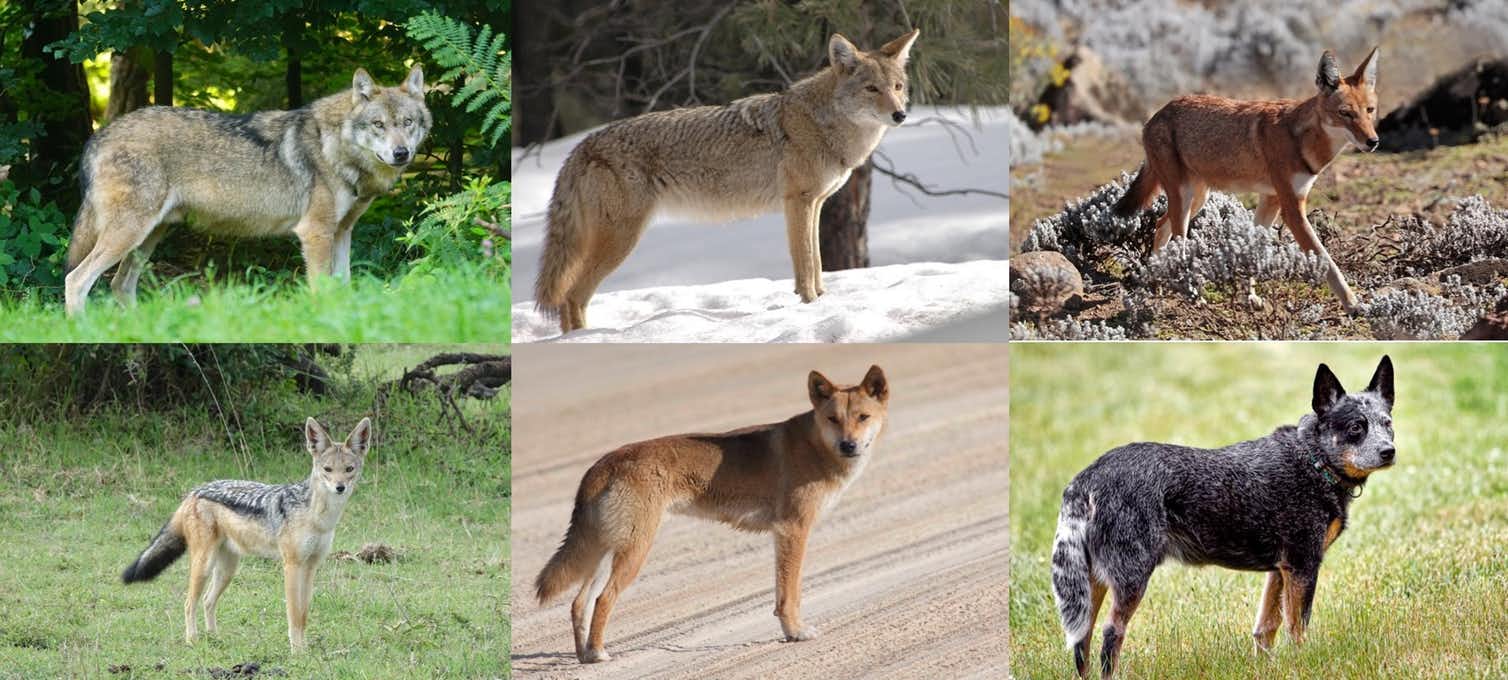
Throughout our lives, we interact with hundreds of wildlife species without stopping to think about it. These interactions can be direct, such as encountering wild animals while hiking in the mountains or driving through rural areas — or more deliberate, as when we engage with wildlife for food, sport, or trade. As hunters, fishers, and collectors, we kill more than 15,000 species of vertebrates — one-third of known diversity — a range of prey 300 times greater than that of any other predator our size (1).
Now, let’s look at it from the other side. Anyone who has survived an attack or a fatal accident, they understand that the experience is remembered for a lifetime. Likewise, animals store information about threatening or harmful encounters with humans (2). For them, adjusting their behaviour in response to human presence has implications for their survival and reproduction (3, 4), which are passed down from generation to generation (5). This ability to adapt, for example, determines which individuals, populations and species coexist with us in urbanised environments (6).
Response to dangerous sounds
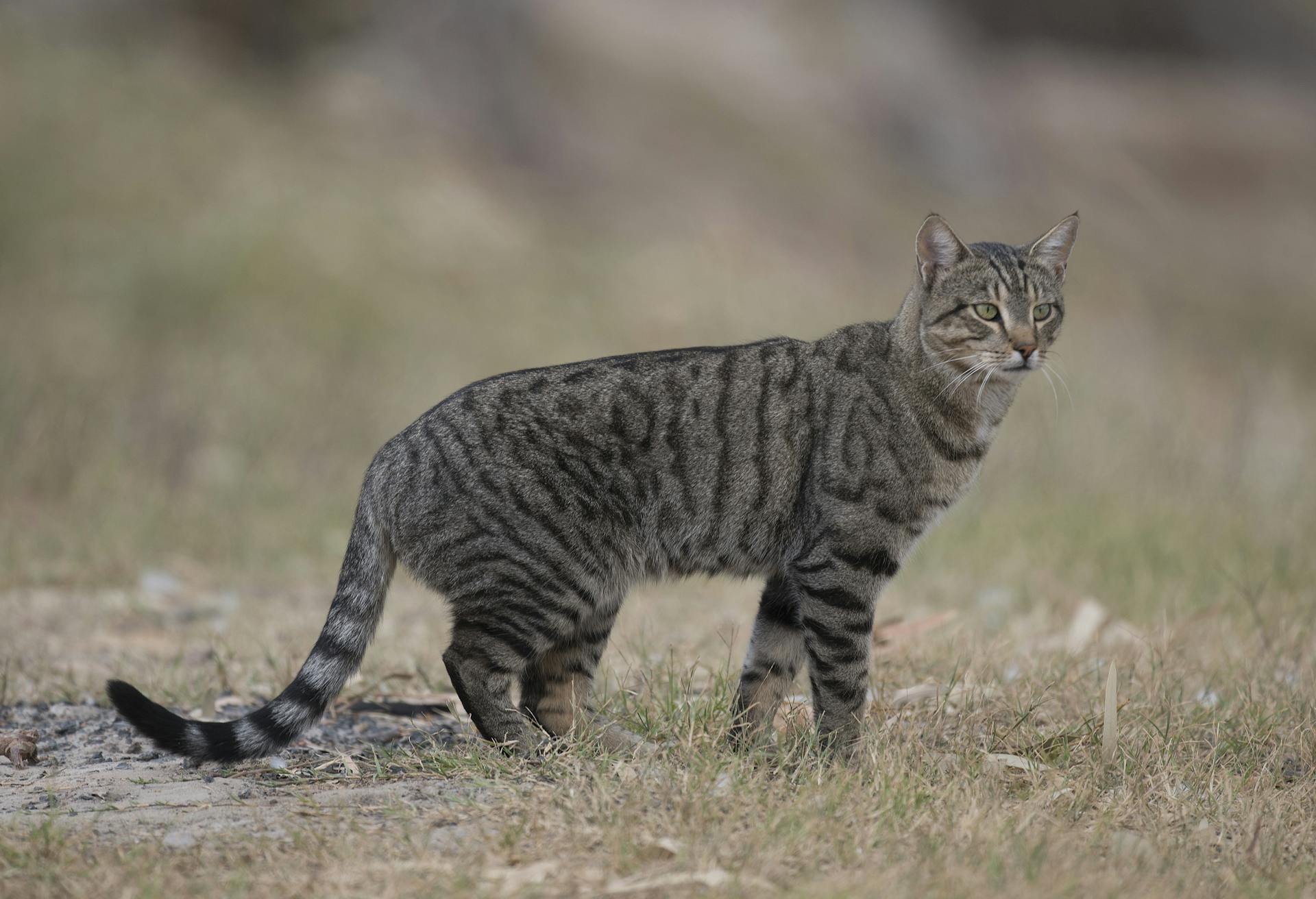
Liana Zanette and her team measured the flight responses of wild mammals in the Greater Kruger National Park (South Africa) when exposed to sounds that signal danger (7) [video-summary]. To do this, Zanette recorded videos of more than 4,000 visits to 21 waterholes by 18 mammal species. During each visit, a speaker attached to a tree randomly played one of five playback sounds: hunting dogs barking, gunshots, lion growls, human conversations in a calm tone and, as a control, the songs of harmless birds.
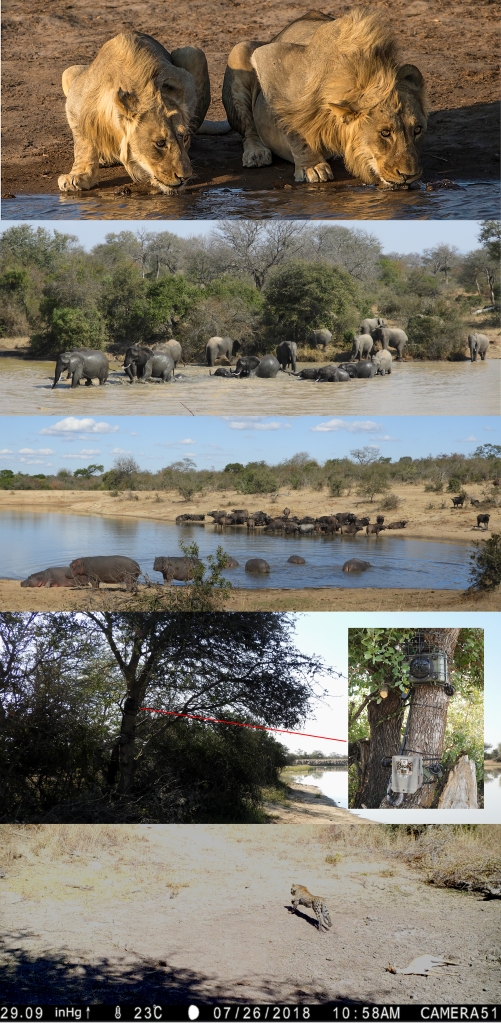

Read the rest of this entry »
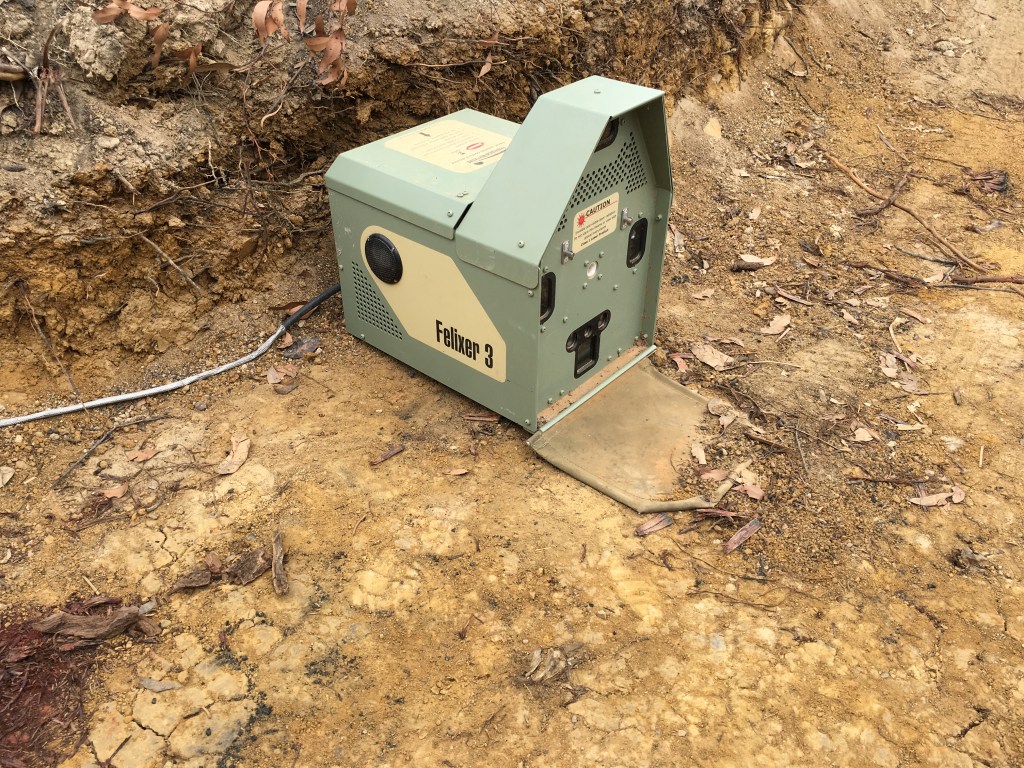
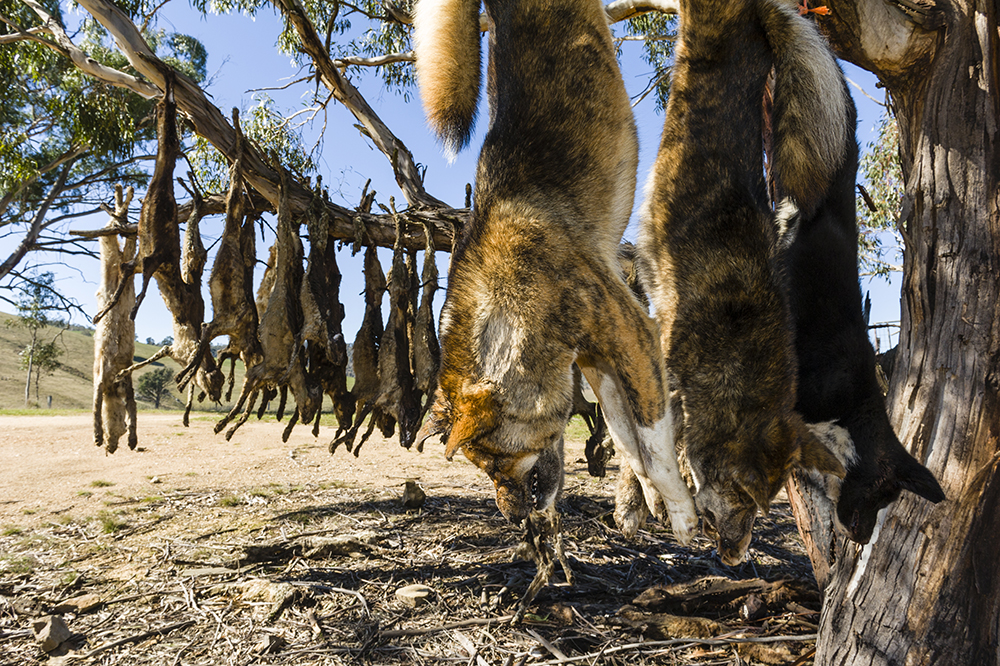



















 Late last year (10 December) I was invited to front up to the ‘Overabundant and Pest Species Inquiry’ at the South Australian Parliament to give evidence regarding so-called ‘overabundant’ and ‘pest’ species.
Late last year (10 December) I was invited to front up to the ‘Overabundant and Pest Species Inquiry’ at the South Australian Parliament to give evidence regarding so-called ‘overabundant’ and ‘pest’ species.

 (reproduced from
(reproduced from 



