This report summarises the findings and recommendations of the South Australian Parliament’s Environment, Resources and Development Committee’s inquiry into biodiversity in South Australia. Specifically, the inquiry investigated the regulatory and policy framework to determine whether it appropriately supports terrestrial and marine ecological processes, biodiversity values and abates species extinction.
The Committee found that in spite of the efforts of the State and Federal governments, industry and private landholders in South Australia, the condition of biodiversity in the State continues to decline. Species extinctions have occurred in the past and a further “extinction debt” still exists. There is no reason to believe that this trend will improve without a change to the way we approach biodiversity conservation.
A key theme to emerge from the Inquiry is that biodiversity conservation needs to be everyone’s responsibility; State and Federal government, industry, the broader community, and private landholders.
This also means that biodiversity conservation needs to occur across both public and private land, with actions coordinated at a landscape scale.
Making biodiversity conservation everyone’s responsibility requires a range of measures, including legislative reform, improved management of threats and greater involvement of the community. The provision of greater resources would yield faster results.
This report has focused on several key themes that emerged from submissions to the Inquiry.
Regulating for better biodiversity – South Australia’s legislative framework
South Australia’s current legislative framework does not provide for optimum biodiversity outcomes.
Three key issues contribute to this –
- an out-of-date suite of environmental legislation that lacks cohesion and consistency, particularly regarding enforcement and compliance provisions;
- inadequate and incomplete processes for identifying and protecting at-risk elements that need special measures (e.g. for protection of specific threatened species and ecological communities); and
- inadequate consideration of biodiversity conservation in legislation that regulates human activities. In particular, there is a lack of cohesion between the environmental legislative and policy framework and land use planning, assessment and approval.
- Statutory fragmentation of biodiversity considerations – that is, consideration of different aspects of biodiversity under different pieces of legislation – results in lack of cohesion and consistency, duplication and inefficiency, and makes it difficult to implement a landscape approach or to identify strategic opportunities and risks.
Taken as a whole, current enforcement provisions do not provide for effective and proportionate compliance action. Enforcement and compliance provisions across the relevant legislation are uneven in their approach. For example, penalties appear to be disproportionate and not risk-based (although there are some exceptions). Modern enforcement tools such as compliance orders, civil remedies and alternative penalties (such as administrative penalties, payment of damages including exemplary damages, remediation orders etc) are not included in all relevant legislation. There is some duplication in offences and inconsistency in the types of sanctions and penalty ranges.
There is an urgent need to amend the legislative framework to support any attempt to improve biodiversity outcomes.
The best approach will be based on clear, shared responsibility for biodiversity outcomes, supported by individual accountability. However, such a change will require policy development and drive.
To ensure forward momentum and improvements in the short term while developing the policy settings to support such a step-change, a staged approach could be implemented. There are various ways this could be achieved.
The Committee suggests a 3-stage approach to reforming the legislative framework. The Committee recommends the creation of a Biodiversity Expert Panel that is responsible for advancing this 3-stage approach.
- The first stage will involve amendments to improve operation and effectiveness of the regulatory regime within current policy settings, acknowledging that as a result of Stage 3, provisions may be altered or moved into different pieces of legislation. Amendments generally would be to the existing ‘environmental’ Acts, and primarily to the National Parks and Wildlife Act 1972 and Native Vegetation Act 1991. They would include many of the specific areas for amendment identified in EDO submissions (2011 & 2015) as well as in the SA Government submission, for example, beginning with amendments to improve current environmental legislation.
- Stage 2 would progress to amendments to improve integration between Acts and improve support for landholders and community participation.
- Stage 3 would implement a system whereby all resource use and management would be managed by one piece of legislation, with protection of biodiversity and sustainable development at its core. Provisions for protected area management, and for the scientific work involved in identifying threatened species and communities, may be contained in separate legislation.
Threats, ecological resilience and restoration
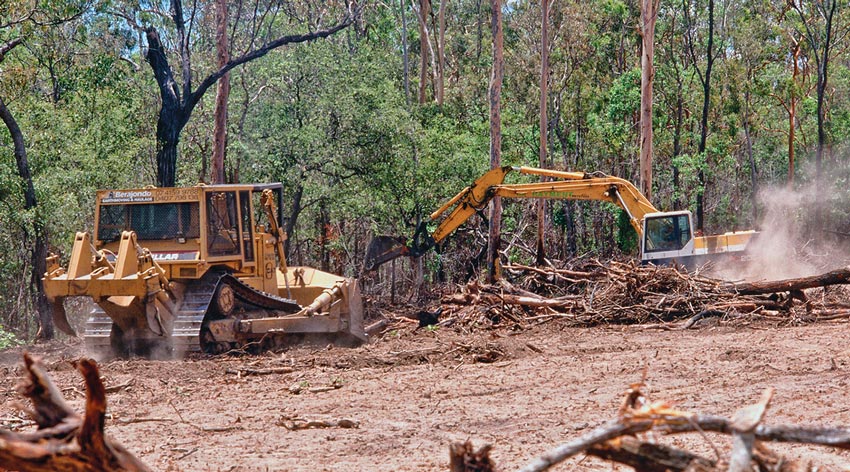
The State’s native biodiversity is facing myriad of current threats, including habitat loss and fragmentation (due to development and changing land-use), pest plants and animals, and control burn regimes. There is a need for more stringent vegetation protection, better informed and enacted control and management strategies of known pest plants and animals, and a revision of burning regimes.
Future threats to the State’s biodiversity will be largely driven by climate change impacts and the interaction with existing major threats (e.g. urbanisation and changing land use). Adequately preparing for and managing such future threats will require knowledge of projected changes and pro-active preparation for such changes.
Working with the community
Involvement of the community is an essential part of any biodiversity conservation strategy for the State. It is a foundation stone for moving to a point where biodiversity conservation is everyone’s business.
Community engagement will become increasingly important for biodiversity conservation, especially given the growing role of volunteers to support works on public land as well as the voluntary conservation efforts of private landholders. The expanding role of volunteers reenforces that biodiversity conservation is everyone’s business.
South Australia’s approach to biodiversity conversation on private land needs to be reinvigorated.
Cross cutting themes
There were several cross cutting themes identified in submissions to the Inquiry. There was broad recognition of the strong cultural and historic significance of elements of biodiversity to Aboriginal people, and that this is often poorly understood outside those communities. Continuing to identify ways for Aboriginal people to contribute to land and water management in South Australia remains a priority.
With respect to knowledge generation, critical knowledge gaps exist that need to be filled and existing knowledge is not being adequately understood, communicated or applied. From a resourcing perspective, there is concern that insufficient funds are being allocated to biodiversity conservation, which is affecting work on public and private lands.
The management of over-abundant species in South Australia remains a challenge, noting the recent impacts of long-nose fur seals in the Lower Lakes and Coorong, and ongoing concerns regarding the impact of animals such as little corellas and some species of kangaroos on negative vegetation.






 So, we go through the motions; we
So, we go through the motions; we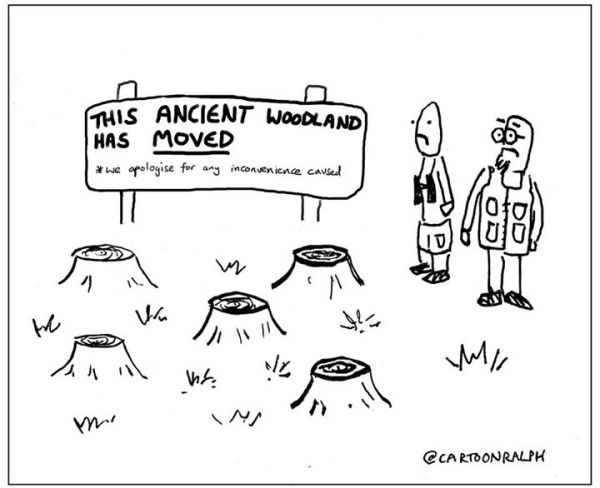 





 So, a few of us have just submitted a letter contesting the Western Australia Government’s recent decision to delist dingoes as ‘fauna’ (I know — what the hell else could they be?). The letter was organised brilliantly by Dr
So, a few of us have just submitted a letter contesting the Western Australia Government’s recent decision to delist dingoes as ‘fauna’ (I know — what the hell else could they be?). The letter was organised brilliantly by Dr  The
The  While some complain that the European Union (EU) is an enormous, cumbersome beast (just ask the self-harming Brexiteers), it generally has some rather laudable legislative checks and balances for nature conservation. While far from perfect, the rules applying to all Member States have arguably improved the state of both European environments, and those from which Europeans source their materials.
While some complain that the European Union (EU) is an enormous, cumbersome beast (just ask the self-harming Brexiteers), it generally has some rather laudable legislative checks and balances for nature conservation. While far from perfect, the rules applying to all Member States have arguably improved the state of both European environments, and those from which Europeans source their materials. So back to the RED legislation. The original ‘
So back to the RED legislation. The original ‘

 Last week we had the pleasure of welcoming the eminent sustainability scientist, Professor
Last week we had the pleasure of welcoming the eminent sustainability scientist, Professor  I’m not sure if many South Australians are aware of this, but the Parliamentary Inquiry into Biodiversity by the
I’m not sure if many South Australians are aware of this, but the Parliamentary Inquiry into Biodiversity by the